Are you looking to create a graphical user interface (GUI) for your Python application? Look no further than PyQT/PySide2, two of the most popular and powerful GUI frameworks available for Python. In this article, we'll delve into the world of PyQT/PySide2 and explore how to build interactive and user-friendly interfaces with Python.
Introduction to PyQT/PySide2
PyQT and PySide2 are Python bindings for the QT application framework, which is written in C++. Both frameworks provide a comprehensive set of libraries and tools for building GUI applications, including widgets, layouts, and event handling. While PyQT is the more mature and widely-used framework, PySide2 is a more recent addition to the Python GUI landscape, offering a more permissive license and improved compatibility with modern Python versions.
Key Features of PyQT/PySide2
So, what makes PyQT/PySide2 so popular among Python developers? Here are some key features that set these frameworks apart:
Cross-platform compatibility: PyQT/PySide2 applications can run on Windows, macOS, and Linux, making them ideal for development teams working on multiple platforms.
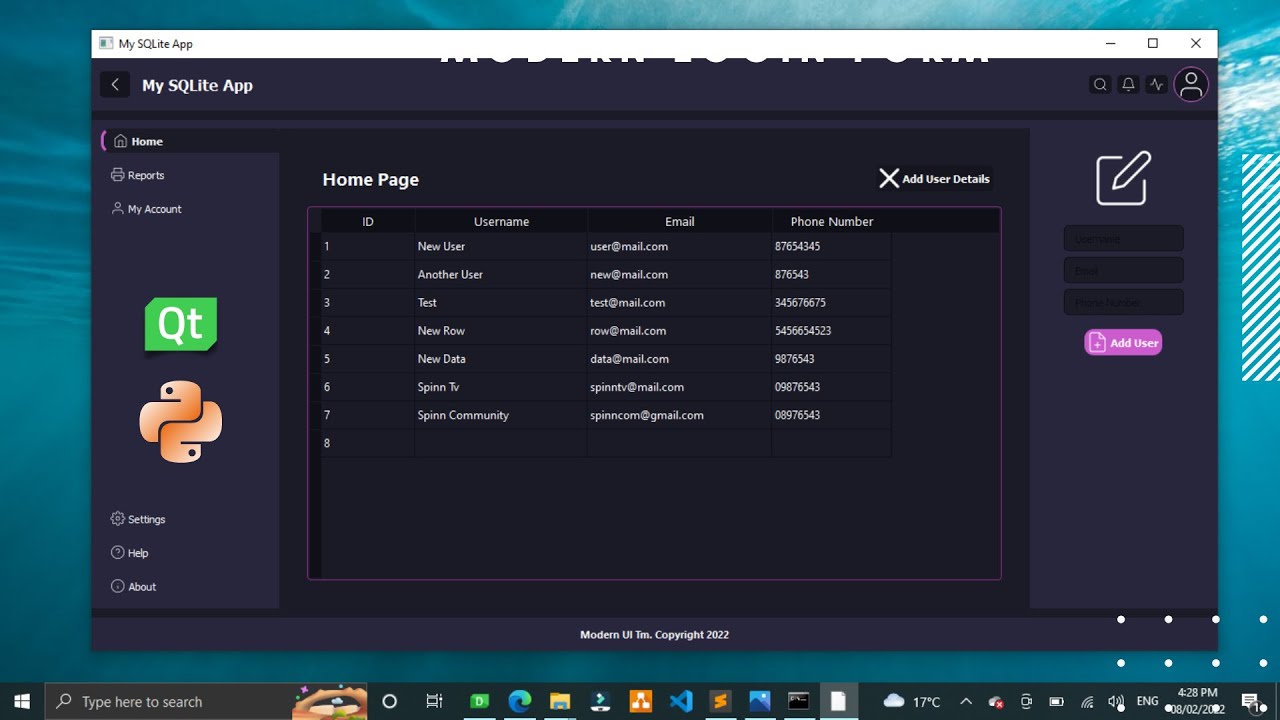
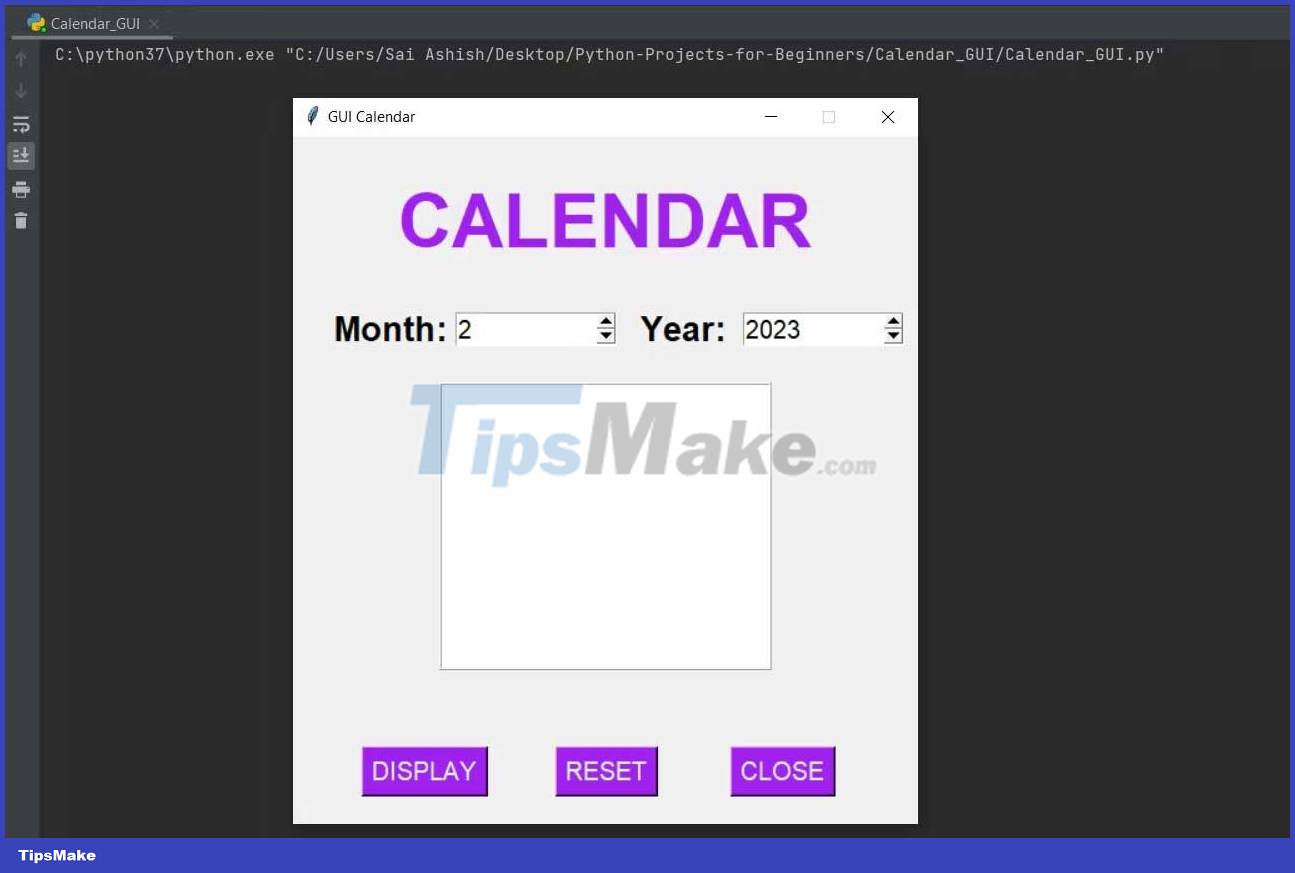
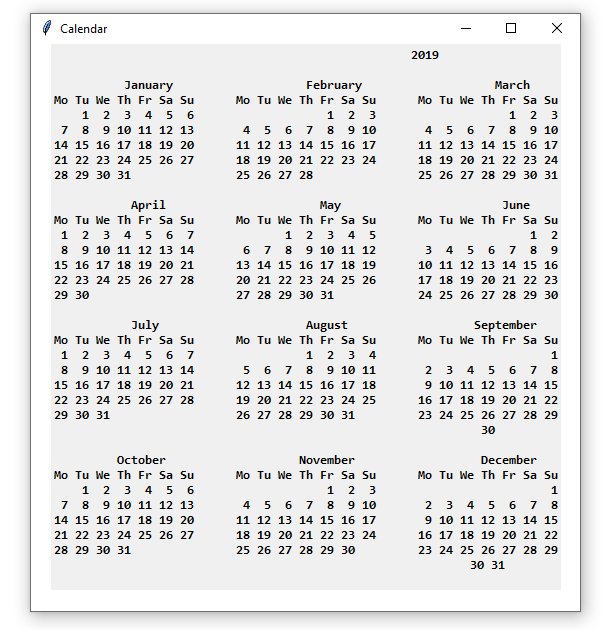
Extensive widget library: Both frameworks offer a wide range of pre-built widgets, including buttons, labels, text editors, and more, making it easy to create complex interfaces.
Signal-slot mechanism: The signal-slot mechanism allows for easy event handling and communication between widgets, making it simple to create interactive and dynamic interfaces.
Support for multimedia and graphics: PyQT/PySide2 provide excellent support for multimedia and graphics, including video playback, audio processing, and 2D/3D graphics rendering.
Getting Started with PyQT/PySide2
Getting started with PyQT/PySide2 is relatively straightforward. Here are the basic steps:
1.
Install PyQT/PySide2: You can install PyQT/PySide2 using pip, the Python package manager. Simply run `pip install pyqt5` or `pip install pyside2` to get started.
2.
Import the framework: Import the PyQT/PySide2 framework in your Python script using `import sys` and `from PyQt5 import QtWidgets` or `from PySide2 import QtWidgets`.
3.
Create a QApplication instance: Create a `QApplication` instance to serve as the main entry point for your GUI application.
4.
Design your interface: Use the various widgets and layouts provided by PyQT/PySide2 to design your interface.
Example Code
Here's a simple example of a PyQT/PySide2 GUI application:
```python
import sys
from PyQt5 import QtWidgets
class MainWindow(QtWidgets.QMainWindow):
def __init__(self):
super(MainWindow, self).__init__()
self.setWindowTitle("My First GUI Application")
self.setGeometry(100, 100, 400, 300)
self.label = QtWidgets.QLabel("Hello, World!", self)
self.label.move(100, 100)
if __name__ == "__main__":
app = QtWidgets.QApplication(sys.argv)
window = MainWindow()
window.show()
sys.exit(app.exec_())
```
This code creates a simple window with a label that displays the text "Hello, World!".
In conclusion, PyQT/PySide2 are two powerful GUI frameworks that make it easy to build interactive and user-friendly interfaces with Python. With their extensive widget libraries, cross-platform compatibility, and support for multimedia and graphics, PyQT/PySide2 are ideal for development teams working on complex GUI applications. Whether you're a seasoned developer or just starting out, PyQT/PySide2 are definitely worth exploring. So why not give them a try and see what you can create?
Note: This article is for general information purposes only and is not intended to be a comprehensive guide to PyQT/PySide2. For more detailed information, please refer to the official PyQT/PySide2 documentation.